What Color Is Sodium Chloride
 Sodium chloride crystals in a form of halite | |
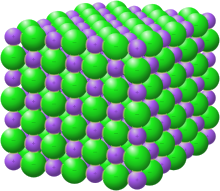 Crystal structure with sodium in purple and chloride in green[1] | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Sodium chloride | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Beilstein Reference | 3534976 |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.726 |
| EC Number |
|
| Gmelin Reference | 13673 |
| KEGG |
|
| MeSH | Sodium+chloride |
| PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| InChI
| |
| SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemic formula | NaCl |
| Molar mass | 58.443 g/mol[ii] |
| Appearance | Colorless cubic crystals[two] |
| Smell | Odorless |
| Density | 2.17 k/cmthree [2] |
| Melting point | 800.7 °C (i,473.3 °F; 1,073.eight K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 1,465 °C (2,669 °F; 1,738 K)[2] |
| Solubility in h2o | 360 g/1000 thou pure water at T = 25 °C[2] |
| Solubility in ammonia | 21.5 m/50 at T = ?[ clarification needed ] |
| Solubility in methanol | 14.9 g/Fifty at T = ?[ description needed ] |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −30.2·10−half-dozen cm3/mol[3] |
| Refractive index (n D) | 1.5441 (at 589 nm)[iv] |
| Structure[5] | |
| Crystal structure | Face up-centered cubic (come across text), cF8 |
| Space group | Fm3k (No. 225) |
| Lattice abiding | a = 564.02 pm |
| Formula units (Z) | 4 |
| Coordination geometry | octahedral at Na+ octahedral at Cl− |
| Thermochemistry[6] | |
| Heat capacity (C) | 50.5 J/(Grand·mol) |
| Std molar | 72.x J/(G·mol) |
| Std enthalpy of | −411.120 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | A12CA01 (WHO) B05CB01 (WHO), B05XA03 (WHO), S01XA03 (WHO) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 0 0 0 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LDfifty (median dose) | iii g/kg (oral, rats)[7] |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Sodium fluoride Sodium bromide Sodium iodide Sodium astatide |
| Other cations | Lithium chloride Potassium chloride Rubidium chloride Caesium chloride Francium chloride |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Sodium chloride (data folio) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Sodium chloride ,[viii] ordinarily known as table salt (although bounding main salt also contains other chemic salts), is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/mol respectively, 100 g of NaCl contains 39.34 thousand Na and lx.66 g Cl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of seawater and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms. In its edible course of tabular array table salt, information technology is commonly used as a condiment and nutrient preservative. Big quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is de-icing of roadways in sub-freezing weather.
Uses [edit]
In addition to the familiar domestic uses of table salt, more ascendant applications of the approximately 250 1000000 tonnes per twelvemonth production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.[9]
Chemicals functions [edit]
Salt is used, direct or indirectly, in the production of many chemicals, which consume most of the globe's product.[ten]
Chlor-alkali manufacture [edit]
It is the starting betoken for the chloralkali procedure, the industrial procedure to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide, according to the chemical equation
This electrolysis is conducted in either a mercury cell, a diaphragm jail cell, or a membrane cell. Each of those uses a different method to divide the chlorine from the sodium hydroxide. Other technologies are nether development due to the high energy consumption of the electrolysis, whereby pocket-sized improvements in the efficiency can accept big economic paybacks. Some applications of chlorine include PVC thermoplastics production, disinfectants, and solvents.
Sodium hydroxide is extensively used in many different industries enabling production of newspaper, lather, and aluminium etc.
Soda-ash industry [edit]
Sodium chloride is used in the Solvay procedure to produce sodium carbonate and calcium chloride. Sodium carbonate, in plow, is used to produce glass, sodium bicarbonate, and dyes, equally well as a myriad of other chemicals. In the Mannheim process, sodium chloride is used for the production of sodium sulfate and muriatic acid.
Standard [edit]
Sodium chloride has an international standard that is created past ASTM International. The standard is named ASTM E534-13 and is the standard test methods for chemical analysis of sodium chloride. These methods listed provide procedures for analyzing sodium chloride to determine whether it is suitable for its intended utilize and application.
Miscellaneous industrial uses [edit]
Sodium chloride is heavily used, so fifty-fifty relatively minor applications tin consume massive quantities. In oil and gas exploration, common salt is an important component of drilling fluids in well drilling. It is used to flocculate and increment the density of the drilling fluid to overcome high downwell gas pressures. Whenever a drill hits a salt formation, salt is added to the drilling fluid to saturate the solution in society to minimize the dissolution within the salt stratum.[9] Table salt is too used to increment the curing of concrete in cemented casings.[10]
In textiles and dyeing, salt is used as a brine rinse to carve up organic contaminants, to promote "salting out" of dyestuff precipitates, and to blend with concentrated dyes to standardize[ clarification needed ] them. Ane of its main roles is to provide the positive ion charge to promote the absorption of negatively charged ions of dyes.[10]
It is besides used in processing aluminium, beryllium, copper, steel and vanadium. In the pulp and paper industry, salt is used to bleach wood pulp. It also is used to brand sodium chlorate, which is added along with sulfuric acrid and h2o to manufacture chlorine dioxide, an splendid oxygen-based bleaching chemical. The chlorine dioxide process, which originated in Frg afterwards World State of war I, is becoming more popular because of environmental pressures to reduce or eliminate chlorinated bleaching compounds. In tanning and leather treatment, salt is added to animal hides to inhibit microbial activeness on the underside of the hides and to attract wet back into the hides.[10]
In safe manufacture, salt is used to make buna, neoprene and white rubber types. Salt brine and sulfuric acrid are used to coagulate an emulsified latex fabricated from chlorinated butadiene.[10] [9]
Common salt besides is added to secure the soil and to provide firmness to the foundation on which highways are built. The salt acts to minimize the effects of shifting caused in the subsurface by changes in humidity and traffic load.[10]
Sodium chloride is sometimes used as a cheap and safe desiccant because of its hygroscopic properties, making salting an constructive method of food preservation historically; the table salt draws water out of bacteria through osmotic pressure level, keeping it from reproducing, a major source of food spoilage. Fifty-fifty though more constructive desiccants are available, few are rubber for humans to ingest.
Water softening [edit]
Difficult water contains calcium and magnesium ions that interfere with activeness of soap and contribute to the buildup of a scale or film of alkaline metal mineral deposits in household and industrial equipment and pipes. Commercial and residential water-softening units use ion-exchange resins to remove ions that cause the hardness. These resins are generated and regenerated using sodium chloride.[10] [9]
Road salt [edit]

Phase diagram of water–NaCl mixture
The second major application of salt is for de-icing and anti-icing of roads, both in grit bins and spread by winter service vehicles. In anticipation of snowfall, roads are optimally "anti-iced" with brine (concentrated solution of salt in water), which prevents bonding betwixt the snow-water ice and the road surface. This process obviates the heavy use of salt after the snowfall. For de-icing, mixtures of brine and table salt are used, sometimes with additional agents such every bit calcium chloride and/or magnesium chloride. The apply of salt or brine becomes ineffective below −10 °C (14 °F).

Mounds of road salt for employ in winter
Salt for de-icing in the United kingdom predominantly comes from a single mine in Winsford in Cheshire. Prior to distribution it is mixed with <100 ppm of sodium ferrocyanide equally an anti-caking agent, which enables rock common salt to flow freely out of the gritting vehicles despite being stockpiled prior to use. In recent years this condiment has too been used in table salt. Other additives had been used in road salt to reduce the total costs. For example, in the U.s.a., a byproduct sugar solution from carbohydrate-beet processing was mixed with stone salt and adhered to route surfaces almost 40% better than loose rock common salt alone. Because information technology stayed on the road longer, the treatment did not have to be repeated several times, saving time and money.[10]
In the technical terms of physical chemistry, the minimum freezing point of a h2o-salt mixture is −21.12 °C (−6.02 °F) for 23.31 wt% of salt. Freezing about this concentration is however then ho-hum that the eutectic signal of −22.4 °C (−viii.3 °F) tin be reached with about 25 wt% of salt.[xi]
Environmental furnishings [edit]
Road salt ends up in fresh-water bodies and could damage aquatic plants and animals past disrupting their osmoregulation ability.[12] The omnipresence of salt poses a trouble in whatsoever coastal coating application, as trapped salts crusade dandy problems in adhesion. Naval authorities and ship builders monitor the salt concentrations on surfaces during structure. Maximal salt concentrations on surfaces are dependent on the authority and awarding. The IMO regulation is mostly used and sets common salt levels to a maximum of 50 mg/m2 soluble salts measured as sodium chloride. These measurements are done by means of a Bresle test. Salinization (increasing salinity, aka freshwater salinization syndrome) and subsequent increased metal leaching is an ongoing problem throughout North America and European fresh waterways.[thirteen]
In highway de-icing, table salt has been associated with corrosion of bridge decks, motor vehicles, reinforcement bar and wire, and unprotected steel structures used in road construction. Surface runoff, vehicle spraying, and windblown actions also bear upon soil, roadside vegetation, and local surface water and groundwater supplies. Although evidence of ecology loading of salt has been plant during pinnacle usage, the bound rains and thaws usually dilute the concentrations of sodium in the surface area where salt was applied.[10] A 2009 written report institute that approximately lxx% of the road salt existence practical in the Minneapolis-St Paul metro surface area is retained in the local watershed.[xiv]
Substitution [edit]
Some agencies are substituting beer, molasses, and beet juice instead of route common salt.[15] Airlines utilize more glycol and sugar rather than salt based solutions for de-icing.[16]
Food industry and agronomics [edit]
Many microorganisms cannot live in a salty environment: h2o is drawn out of their cells by osmosis. For this reason salt is used to preserve some foods, such as salary, fish, or cabbage.
Salt is added to food, either past the food producer or by the consumer, every bit a flavor enhancer, preservative, binder, fermentation-control additive, texture-control agent and color developer. The salt consumption in the food industry is subdivided, in descending lodge of consumption, into other nutrient processing, meat packers, canning, blistering, dairy and grain mill products. Salt is added to promote color development in bacon, ham and other processed meat products. As a preservative, salt inhibits the growth of leaner. Salt acts every bit a binder in sausages to grade a binding gel fabricated up of meat, fat, and wet. Common salt also acts equally a flavor enhancer and equally a tenderizer.[10]
In many dairy industries, salt is added to cheese as a color-, fermentation-, and texture-control agent. The dairy subsector includes companies that manufacture creamery butter, condensed and evaporated milk, frozen desserts, ice foam, natural and processed cheese, and specialty dairy products. In canning, table salt is primarily added as a flavor enhancer and preservative. Information technology besides is used as a carrier for other ingredients, dehydrating agent, enzyme inhibitor and tenderizer. In blistering, salt is added to control the rate of fermentation in bread dough. It also is used to strengthen the gluten (the elastic protein-water complex in certain doughs) and as a flavor enhancer, such as a topping on broiled appurtenances. The food-processing category also contains grain mill products. These products consist of milling flour and rice and manufacturing cereal breakfast food and blended or prepared flour. Salt is too used a seasoning amanuensis, e.g. in potato chips, pretzels, cat and dog food.[x]
Sodium chloride is used in veterinary medicine as emesis-causing agent. It is given as warm saturated solution. Emesis can as well exist caused by pharyngeal placement of small corporeality of plainly table salt or table salt crystals.
Medicine [edit]
Sodium chloride is used together with h2o as one of the master solutions for intravenous therapy. Nasal spray often contains a saline solution.
Firefighting [edit]

A class-D burn down extinguisher for various metals
Sodium chloride is the principal extinguishing agent in burn down extinguishers (Met-L-X, Super D) used on flammable metallic fires such as magnesium, potassium, sodium, and NaK alloys (Form D). Thermoplastic powder is added to the mixture, along with waterproofing (metal stearates) and anti-caking materials (tricalcium phosphate) to form the extinguishing agent. When information technology is applied to the fire, the salt acts like a estrus sink, dissipating heat from the burn, and also forms an oxygen-excluding crust to smother the fire. The plastic additive melts and helps the crust maintain its integrity until the burning metal cools below its ignition temperature. This type of extinguisher was invented in the tardily 1940s as a cartridge-operated unit of measurement, although stored pressure versions are now pop. Common sizes are xxx pounds (14 kg) portable and 350 pounds (160 kg) wheeled.[ citation needed ]
Cleanser [edit]
Since at least medieval times, people have used salt as a cleansing agent rubbed on household surfaces. Information technology is besides used in many brands of shampoo, toothpaste and popularly to de-ice driveways and patches of water ice.
Optical usage [edit]
Defect-gratuitous NaCl crystals take an optical transmittance of about xc% for infrared calorie-free, specifically between 200 nm and 20 µm. They were therefore used in optical components (windows and prisms) operating in that spectral range, where few non-absorbing alternatives exist and where requirements for absence of microscopic inhomogeneities are less strict than in the visible range. While cheap, NaCl crystals are soft and hygroscopic – when exposed to the ambient air, they gradually cover with "frost". This limits awarding of NaCl to dry environments, vacuum sealed associates areas or for short-term uses such equally prototyping. Present materials like zinc selenide (ZnSe), which are stronger mechanically and are less sensitive to moisture, are used instead of NaCl for the infrared spectral range.
Chemistry [edit]
Solid sodium chloride [edit]

Sodium chloride crystal under microscope.

NaCl octahedra. The yellow stipples represent the electrostatic force betwixt the ions of contrary charge
In solid sodium chloride, each ion is surrounded by 6 ions of the opposite charge equally expected on electrostatic grounds. The surrounding ions are located at the vertices of a regular octahedron. In the linguistic communication of close-packing, the larger chloride ions (167 pm in size[17]) are arranged in a cubic array whereas the smaller sodium ions (116 pm[17]) fill all the cubic gaps (octahedral voids) between them. This same bones construction is found in many other compounds and is ordinarily known as the halite or rock-salt crystal structure. Information technology can be represented every bit a confront-centered cubic (fcc) lattice with a two-atom basis or every bit ii interpenetrating confront centered cubic lattices. The first atom is located at each lattice point, and the second atom is located halfway between lattice points along the fcc unit of measurement cell edge.
Solid sodium chloride has a melting bespeak of 801 °C. Thermal conductivity of sodium chloride equally a part of temperature has a maximum of 2.03 W/(cm K) at 8 Grand (−265.15 °C; −445.27 °F) and decreases to 0.069 at 314 K (41 °C; 106 °F). It likewise decreases with doping.[18]
Atomic-resolution existent-time video imaging allows visualization of the initial stage of crystal nucleation of sodium chloride.[nineteen]
Aqueous solutions [edit]
| Solubility of NaCl (thousand NaCl / 1 kg of solvent at 25 °C (77 °F))[twenty] | |
|---|---|
| Water | 360 |
| Formamide | 94 |
| Glycerin | 83 |
| Propylene glycol | 71 |
| Formic acid | 52 |
| Liquid ammonia | xxx.2 |
| Methanol | 14 |
| Ethanol | 0.65 |
| Dimethylformamide | 0.4 |
| 1-Propanol | 0.124 |
| Sulfolane | 0.05 |
| i-Butanol | 0.05 |
| 2-Propanol | 0.03 |
| ane-Pentanol | 0.018 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.003 |
| Acetone | 0.00042 |
The attraction between the Na+ and Cl− ions in the solid is so strong that but highly polar solvents like water dissolve NaCl well.

View of ane slab of NaCl(H2O)two (blood-red = O, white = H, light-green = Cl, regal = Na).[21]
When dissolved in water, the sodium chloride framework disintegrates equally the Na+ and Cl− ions become surrounded by polar water molecules. These solutions consist of metal aquo complex with the formula [Na(H2O)8]+, with the Na–O altitude of 250 pm. The chloride ions are also strongly solvated, each existence surrounded by an boilerplate of half dozen molecules of water.[22] Solutions of sodium chloride have very unlike backdrop from pure h2o. The eutectic betoken is −21.12 °C (−6.02 °F) for 23.31% mass fraction of salt, and the boiling point of saturated salt solution is near 108.vii °C (227.seven °F).[11] From common cold solutions, salt crystallises as the dihydrate NaCl·2H2O.[23]
pH of sodium chloride solutions [edit]
The pH of a sodium chloride solution remains ≈7 due to the extremely weak basicity of the Cl− ion, which is the conjugate base of operations of the strong acid HCl. In other words, NaCl has no upshot on system pH[24] in diluted solutions where the effects of ionic strength and activity coefficients are negligible.
Unexpected stable stoichiometric variants [edit]
Common salt has a 1:one molar ratio of sodium and chlorine. In 2013, compounds of sodium and chloride of different stoichiometries accept been discovered; five new compounds were predicted (due east.grand., Na3Cl, Na2Cl, Na3Cl2, NaCl3, and NaClvii). The existence of some of them has been experimentally confirmed at high pressures: cubic and orthorhombic NaCl3 and ii-dimensional metallic tetragonal Na3Cl. This indicates that compounds violating chemical intuition are possible, in simple systems under nonambient conditions.[25]
Occurrence [edit]
Small particles of sea salt are the dominant cloud condensation nuclei far out at body of water, which allow the formation of clouds in otherwise non-polluted air.[26]
Production [edit]
Salt is currently mass-produced by evaporation of seawater or brine from brine wells and salt lakes. Mining of rock salt is also a major source. China is the world'southward main supplier of salt.[ten] In 2017, globe production was estimated at 280 million tonnes, the top five producers (in million tonnes) being China (68.0), United States (43.0), Republic of india (26.0), Germany (xiii.0), and Canada (13.0).[27] Common salt is likewise a byproduct of potassium mining.
See also [edit]
- Biosalinity
- Edible salt (tabular array salt)
- Halite, the mineral grade of sodium chloride
- Health effects of salt
- Salinity
- Salting the world
- Salt poisoning
References [edit]
- ^ "Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Crystal". PhysicsOpenLab. Retrieved 23 Baronial 2021.
- ^ a b c d due east f Haynes, 4.89
- ^ Haynes, iv.135
- ^ Haynes, 10.241
- ^ Haynes, iv.148
- ^ Haynes, 5.viii
- ^ Sodium chloride. nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008), Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (third ed.), Longman, pp. 143 and 755, ISBN9781405881180
- ^ a b c d Westphal, Gisbert et al. (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_317.pub4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Kostick, Dennis S. (October 2010) "Common salt" in U.S. Geological Survey, 2008 Minerals Yearbook
- ^ a b Elvers, B. et al. (ed.) (1991) Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 5th ed. Vol. A24, Wiley, p. 319, ISBN 978-3-527-20124-2.
- ^ Rastogi, Nina (16 February 2010) Does road salt harm the surroundings? slate.com.
- ^ "Saltier waterways are creating unsafe 'chemical cocktails'". phys.org.
- ^ "Most Road Common salt Is Making It into Lakes And Rivers". www.sciencedaily.com. University of Minnesota. 20 February 2009. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ Casey, Michael. "Turning to beet juice and beer to address road common salt danger". phys.org.
- ^ "EASA Cautions on Organic Common salt Deicing Fluid". MRO Network. 9 December 2016.
- ^ a b R. D. Shannon (1976). "Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides". Acta Crystallogr A. 32 (five): 751–767. Bibcode:1976AcCrA..32..751S. doi:10.1107/S0567739476001551.
- ^ Sirdeshmukh, Dinker B.; Sirdeshmukh, Lalitha & Subhadra, K. Thou. (2001). Alkali halides: a handbook of physical backdrop. Springer. pp. 65, 68. ISBN978-3-540-42180-1.
- ^ Nakamuro, Takayuki; Sakakibara, Masaya; Naught, Hiroki; Harano, Koji; Nakamura, Eiichi (2021). "Capturing the Moment of Emergence of Crystal Nucleus from Disorder". Journal of the American Chemic Lodge. 143 (four): 1763–1767. doi:x.1021/jacs.0c12100. PMID 33475359.
- ^ Burgess, J (1978). Metallic Ions in Solution. New York: Ellis Horwood. ISBN978-0-85312-027-8.
- ^ Klewe, B; Pedersen (1974). "The crystal structure of sodium chloride dihydrate". Acta Crystallogr. B30 (10): 2363–2371. doi:10.1107/S0567740874007138.
- ^ Lincoln, South. F.; Richens, D. T. and Sykes, A. Chiliad. (2003) "Metal Aqua Ions" Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry Ii Volume i, pp. 515–555. doi:10.1016/B0-08-043748-vi/01055-0.
- ^ Water-NaCl phase diagram. Lide, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 86 ed (2005-2006), CRC pages eight-71, eight-116.
- ^ "Acidic, Bones, and Neutral Salts". Flinn Scientific Chem Fax. 2016. Retrieved eighteen September 2018.
Neutralization of a stiff acid and a stiff base gives a neutral salt.
- ^ Zhang, West.; Oganov, A. R.; Goncharov, A. F.; Zhu, Q.; Boulfelfel, South. East.; Lyakhov, A. O.; Stavrou, E.; Somayazulu, Thou.; Prakapenka, V. B.; Konôpková, Z. (2013). "Unexpected Stable Stoichiometries of Sodium Chlorides". Science. 342 (6165): 1502–1505. arXiv:1310.7674. Bibcode:2013Sci...342.1502Z. doi:x.1126/science.1244989. PMID 24357316. S2CID 15298372.
- ^ Mason, B. J. (2006). "The role of sea-common salt particles every bit cloud condensation nuclei over the remote oceans". Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Lodge. 127 (576): 2023–32. Bibcode:2001QJRMS.127.2023M. doi:10.1002/qj.49712757609. S2CID 121846285.
- ^ Salt, U.Due south. Geological Survey
-
 This article incorporates public domain fabric from Common salt (PDF). United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain fabric from Common salt (PDF). United States Geological Survey.
Cited sources [edit]
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). CRC Press. ISBN978-1439855119.
External links [edit]
![]()
Wikimedia Eatables has media related to NaCl.
- Salt United States Geological Survey Statistics and Information
- "Using Salt and Sand for Winter Road Maintenance". Road Management Journal. December 1997. Archived from the original on 21 September 2016. Retrieved thirteen Feb 2007.
- Calculators: surface tensions, and densities, molarities and molalities of aqueous NaCl (and other salts)
- JtBaker MSDS
What Color Is Sodium Chloride,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_chloride
Posted by: gasparddienteor.blogspot.com


![{\displaystyle {\ce {2 NaCl + 2 H2O ->[electrolysis] Cl2 + H2 + 2 NaOH}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6175336b0ecf3b2032d6a60ac2a534b10e6f61f3)



0 Response to "What Color Is Sodium Chloride"
Post a Comment