Kinetic Energy Of A Photon
What is Photon Energy?
Any of the energy units can be used to express photon energy. However, we generally employ the electronvolt (eV) unit of photon free energy and the joule (multiples, such as microjoule) amidst the units.
Photon Free energy
The big units are typically useful in representing photon energy with higher frequency and higher energy, such as gamma rays, every bit opposed to lower energy photons, such every bit those in the radiofrequency area of the electromagnetic spectrum, considering 1 Joule = 6.24 ten 10 eV.
Also check:
Properties of Photon
Photons accept a multitude of characteristics, including:
- Photons have no electrical charge.
- The velocity of photons is equivalent to the speed of light.
- Photons have no mass, but their energy is East = hf = hc/ λ. Planck's abiding is h = 6.626*ten-34 Js in this case. The photon energy is inversely related to the electromagnetic moving ridge'southward wavelength. The photon is more energetic when its wavelength is shorter, and less energetic when its wavelength is longer.
Backdrop of Photon
- Photons can be generated and destroyed with minimal loss of energy or momentum. When EM waves are emitted by a source, photons are created, and when they come into contact with matter, they tin exist absorbed and their energy transferred.
- In 1905, Einstein used the detached nature of light to explicate the photoelectric issue. By shining light on a metal surface, information technology was demonstrated. If the frequency of the light is higher than the cut-off frequency fc, photoelectric electrons are produced; if the frequency of the light is lower than this cut-off frequency fc, no photoelectric electrons are generated.
- The wavelength of a photon is 0.377 um (377 nm). 3.2883eV photon free energy.
Also check:
Formula of Photon Energy
The photon free energy formula tin can be expressed in the manner given below:
E = hf
In addition, the frequency of the energy photon formula is c/ λ. Irresolute the value of 'f' in the equation higher up:
Eastward = hc/ λ .... (two)
Eastward is the energy of a photon in Joules.
λ is the wavelength of a photon in meters
c is the speed of light in a vacuum, which is 3 10 10 meters per second, and h is the Planck abiding, which is 6.626 10 kgm / s or J.s.
Check Important Notes for Atomic Number and Mass Number
At 1 Hz, the photon energy is equal to 6.626 10 10 J.
Planck's constant is 4.14 ten x eV.south.
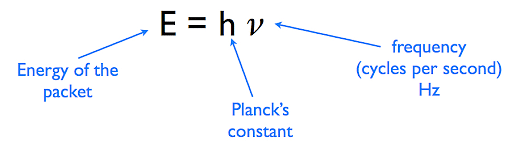
The Formula of Photon Free energy
Energy of Photon Formula
We notice from the energy of photon equation that the energy of a photon depends on the following parameters:
- The energy of a photon is directly associated with the photon'south electromagnetic frequency.
- The energy of photons is based on wavelength in such a way that the energy of photons is inversely proportional to the wavelength.
- The higher is the photon energy frequency, the more its energy. Withal, on the other hand, the longer is the photon'south wavelength, the lower its energy.
As well check:
Photon Wavelength Formula
By knowing the frequency of the photon, i can easily calculate the wavelength with the help of the equation λ=cν where c is the speed of light and ν is the frequency.
Example: If a photon has a frequency of vi×1012s−1 the wavelength is
λ=three×108ms/ 6×1012s−1
= 5×10−5 grand=fifty micrometres.
Which Photons Take the Most Energy?
The formula clearly shows how the energy of a photon is affected by its frequency and wavelength. Let'south take a wait at each of the formulas above and meet what they hateful in terms of photon physics.
For starters, because wavelength and frequency always multiply to equal a abiding, if photon A has a frequency two times that of photon B, photon A's wavelength must be 1/2 of photon B'due south wavelength.
2nd, y'all tin can learn a lot most how a photon's frequency tin give you a rough approximate of its free energy. We know photon A is twice equally energetic as photon B since it has a greater frequency. We can observe that energy scales direct with frequency in general. Similarly, because the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength, photon A is more energetic than photon B if its wavelength is shorter.
Also Check:
Kinetic Energy of Photon Formula
Nosotros need the free energy in order to assistance them come out of the metal, i.e., to pb the photoemission procedure every bit we know that the electrons are tightly bonded to the metal. Therefore, the electrons that are released from the metallic have some free energy. Therefore, the maximum kinetic energy of ejected electrons is given below:
KEeast = hf - Exist
Here,
E = the photon energy
Be = binding energy/ the Work part of the electron, that is particular to the given material.
KEe = kinetic energy (in Joules)
As well, Read Further:
Applications of Photons
Photons with the energy of roughly 4.1357 x 10 eV are released by an FM radio station transmitting at 100 MHz electromagnetic frequency. We know that this quantity of energy is approximately 8 to 10 times the mass of the electron, or 9.1 x 10 kg, based on the mass-energy equivalency.
Things to Remember
- Photons make upwardly not only light, just also all electromagnetic energy (i.e., microwaves, radio waves, and Ten-rays).
- Albert Einstein came upwards with the concept of the photon in the first identify. Scientist Gilbert N. Lewis was the first to coin the term "photon" to characterize information technology.
- The moving ridge-particle duality hypothesis claims that low-cal behaves as a wave and a particle at the aforementioned time.
- Photons are electrically neutral at all times. They are devoid of whatsoever electric accuse. Photons do not self-destruct.
- In 1905, Einstein applied the discrete nature of light to explain the photoelectric effect. By shining light on a metal surface, it was demonstrated. If the frequency of the lite is higher than the cutting-off frequency fc, photoelectric electrons are produced.
Read Also: Charge to Mass Ratio of Electron
Sample Questions
Ques: What is this photon's energy? (ii marks)
Ans: The velocity of photons is equivalent to the speed of light. Photons take no mass, but their energy is E = hf = hc/. Planck's constant is h = 6.626*10-34 Js in this case. The photon energy is inversely related to the electromagnetic wave's wavelength.
Ques: What purpose does photon energy serve? (2 marks)
Ans: Although photon energy (lite energy as quantum energy) is more valuable than rut energy, most solar beams tend to catechumen to ambient heat. Solar beams' well-nigh efficient work volition be done past using breakthrough characteristics of them, merely every bit plants' photosynthetic processes do.
Ques: What is the mechanism past which a photon transports energy? (ii marks)
Ans: Despite its lack of bulk, light does comport energy via its motion. Because photons (light particles) accept no mass, they must obey E = pc and derive their whole free energy from their momentum. In the general equation, there is now an interesting additional bear upon.
Ques: Is a photon a particle or a wave? (2 marks)
Ans: Light is a particle (photon), and the passage of photons is a wave, according to Einstein. Einstein'due south calorie-free quantum theory's fundamental premise is that light'south free energy is proportional to its oscillation frequency.
As well Read:
Ques: Is information technology truthful that photons have spin? (two marks)
Ans: Electrons and quarks (matter particles) tin can have spins of –i/2 or +1/two; photons (low-cal particles) can take spins of –one or +i, and Higgs bosons must have spins of 0. Particle spins, despite their pocket-sized size, have a pregnant impact on our daily lives. We can brand 3D movies cheers to photons' spin characteristics.
Ques: A sodium lamp emits yellow light with a frequency of 5.x∗10 14 Hz. How much energy is independent in ane.5 mol of photons? h=6.63∗10−34 J⋅south. (3 marks)
Ans: The energy of a single photon is given by the equation:
E=hv
We are given the frequency and the value of the constant, allowing us to solve.
E= (6.63∗10−34 J⋅s) (5.10∗1014 Hz) =3.38∗10−19 J
The to a higher place gives the energy contained in one photon. Side by side, solve for the energy contained in one.5mol using Avogadro's number:
(i.5mol∗six.022∗1023photons/1mol) x (3.38∗x−xixJ/1photon) = 3.1∗ten5J
Ques: What happens when a photon is created? (2 marks)
Ans: When an electron in a college-than-normal orbit returns to its normal orbit, a photon is produced. During the transition from high to low energy, the electron emits a photon, which is a packet of energy with highly precise properties. Photons are generated when sodium atoms are energized by a sodium vapor lite.
Ques: If the free energy of a photon is 350×10 −10 J, make up one's mind the wavelength of that photon. (iii marks)
Ans: Given parameters are,
E = 350×x−xJ
c = three×10viiim/southward
h = vi.626×10−34Js
Photon free energy formula is given by,
E = hc / λ
λ = hc / Eastward
λ = 6.626×10−34×three×xeight / 350×10−10
λ = 19.87 ten x-28 / 350 x 10−10
λ = 0.056 x 10-16 thousand
Chemistry Related Links:
Kinetic Energy Of A Photon,
Source: https://collegedunia.com/exams/photon-energy-formula-and-solved-examples-chemistry-articleid-2385
Posted by: gasparddienteor.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Kinetic Energy Of A Photon"
Post a Comment