How To Use Genetic Code Table
What is Genetic Code?
Genetic lawmaking is ane of the set up of rules which is used by all the prison cell in the living organisms to translate the data which is encoded within the genetic material as Deoxyribonucleic acid or mRNA which is the sequences of the nucleotides triplet or codons which brand up the proteins.
This translation is achieved past the prison cell organelle named every bit ribosomes, which connects the proteinogenic amino acids in club that is specified by the mRNA, with the help of transfer RNA which carries the amino acids and make information technology to read by the mRNA three nucleotides at the specific time.
The genetic code is similar to all organism and it is expressed within the cells in a simple style.
This codon specifies the amino acid which volition exist added to the adjacent during protein synthesis. Nevertheless, with some of the expectations, three nucleotide codons in a nucleic acrid sequence specifies a particular amino acid.
Majority of the genes are encoded with the appropriate mode co-ordinate to its function. The observation of how proteins are encoded begins after the discovery of structure in year 1953.
George Gamow postulated the iii bases which are needed to encode the 20 amino acids which are used by the living cells that are used to build up the proteins. Information technology allows a maximum of 64 amino acids.
Features of Genetic Code
Genetic code is defined equally the sequence of nucleotides nowadays in the nucleic acids such as DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acids) or the RNA (Ribonucleic acids) which determines the amino acid sequence of the proteins.
Fifty-fifty the linear sequence of nucleotides in the Dna contains the information for the protein sequences, where proteins are not made directly from the Dna, rather the linear sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA contains specific data for the protein sequences, Proteins are not synthesized directly from the DNA and which directs the formation of the poly peptide.
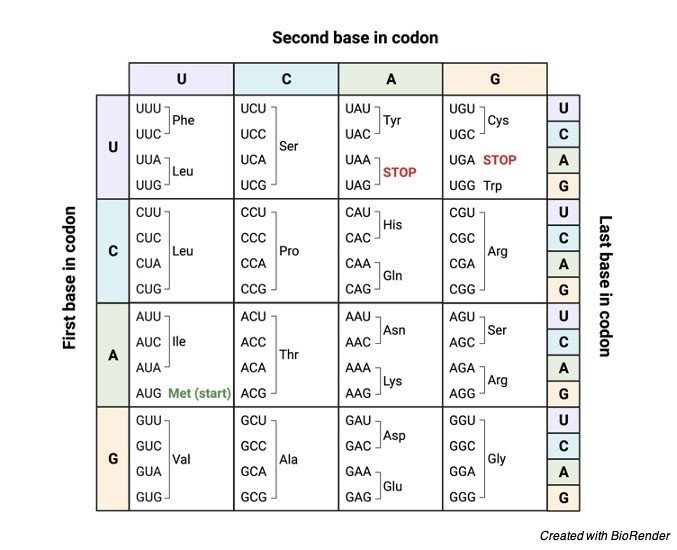
Genetic Lawmaking Nautical chart
RNA is also equanimous of 4 nucleotides namely adenine, guanine, Cytosine and Uracil. Where equally the three adjacent nucleotides constitute a unit known equally the codon, which codes for the amino acid.
For example: the sequence of the codon AUG which specifies the methionine amino acid.
In that location are almost 64 possible codons, out of which three does not code for amino acids, but these indicates the end of the poly peptide.
The remaining 61 codons specifies the 20 amino acids which brand up the proteins the codon AUG additionally indicates the start of the poly peptide along with the coding of the methionine.
Methionine and tryptophan are considered equally the two amino acids which are coded by just a single codons AUG and UGG respectively.
The remaining eighteen amino acids are coded by the 2 to six codons. The amino acids are coded by more than a single codon and it is called as a codon-degenerate.
The genetic lawmaking once idea to exist identical in all forms of life, which has been found diversely in certain organisms and also in mitochondria in some eukaryotes.
Types of Genetic Lawmaking
The genetic code is differentiated into two types and they can be expressed in the class of either RNA codons which occur in the messenger RNA and the codons reads the data during the production of polypeptides during the process of translation.
Each of the messenger RNA molecules acquires their sequence of nucleotides by the procedure of transcription from the corresponding Deoxyribonucleic acid.
Because during the process, Dna sequencing becomes rapid because nearly of the genes are now beingness discovered during the level of Deoxyribonucleic acid before they are discovered equally mRNA or equally a production of protein, which is extremely useful to accept the tabular array of codons which is expressed equally DNA.
Dna Codons
Types of Codon
The genetic code has virtually 64 triplets of nucleotides. The triplets are known as codons, with the three expectations, each of the codon encodes for 1 of the xx amino acids for the production of proteins.
This produces some of the redundancy in code. Almost all the amino acids are encoded more than a single codon.
Where ane codon is AUG which serves the 2 related functions. It besides signals for the start of translation, and its codes for the incorporating of the amino acid methionine into the growing chain of the polypeptide chain.
The codons are of 2 types namely;
Sense codons
Signal codons
I. Sense Codon
II. Betoken Codon
Sense codon codes for the signaling during the production of proteins. There are virtually iv codons that codes for a betoken, namely AUG, UAA, UAG and UGA. Signal codons are further classified equally 2 types namely
Starting time codons: The codon which starts the procedure of translation is known as starting time codon. Information technology is too commonly called as initiation codons every bit information technology initiates the production of polypeptide chain. The all-time said example for start codon is AUG. This codes for the amino acid methionine, in prokaryotes it is Due north-formyl methionine.
Finish codons: Stop codon provides a betoken for termination of a polypeptide chain. These codons are commonly called as termination codons as they provide a point for the termination and the release of the polypeptide chain.
Properties of Genetic Lawmaking
Genetic code-Triplet: It consists of 64 codons, which are sufficient to code the xx amnio acids and it helps in signaling the beginning and stop codons and synthesizing the polypeptide chain. Where as a in a triplet code three bases of RNA codes for a single amino acid.
The lawmaking is as well universal which are assigned for the same amino acids.
The genetic code is comma less where the codons are continuous and are demarcation lines betwixt the codons.
The genetic code is unremarkably not-over lapping. Whereas in non-overlapping two amino acids are being coded by the six bases.
The genetic code is also non-ambiguous, Redundant and it has a polarity.
Genetic Code Citations
- The development of the genetic code: Impasses and challenges. Biosystems . 2018 February;164:217-225.
- The Nothing of the Genetic Code. Biosystems . 2018 Sep;171:31-47.
- Origin and Evolution of the Universal Genetic Code. Annu Rev Genet . 2017 Nov 27;51:45-62.
- The path to the genetic code. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj . 2017 Nov;1861(11 Pt A):2674-2679.
- Understanding the Genetic Code. J Bacteriol . 2019 Jul ten;201(15):e00091-nineteen.
- Rewriting the Genetic Code. Annu Rev Microbiol . 2017 Sep 8;71:557-577.
Similar Post:
How To Use Genetic Code Table,
Source: https://researchtweet.com/genetic-code-chart-table-definition-and-examples/
Posted by: gasparddienteor.blogspot.com



0 Response to "How To Use Genetic Code Table"
Post a Comment